When setting up a website, hosting goes back to square one. Traditional servers have been around for a long time but the shift toward cloud computing is altering the entire field. Case in point: cloud web hosting and cloud-based applications have a lot to offer digital business platforms and marketers.
This article will dive into the basic differences between traditional and cloud-based web hosting and how it benefits companies.
What is Cloud Web Hosting?
The definition of Web hosting is as simple as this: putting up a website on the Internet for the public. Traditional web hosting involves the use of dedicated servers or computers that store the site and its information. Naturally, you need a domain and a server and you’ll be ready to go.
Cloud hosting is similar but, instead of physical servers or computers, the website or application is stored using cloud technologies. Consequently, the website data is stored in a network of servers that is not hosted in a single physical source. Ergo, all the server resources are available virtually.
There are 3 types of web hosting in the traditional format: Shared hosting, VPS, and dedicated hosting.
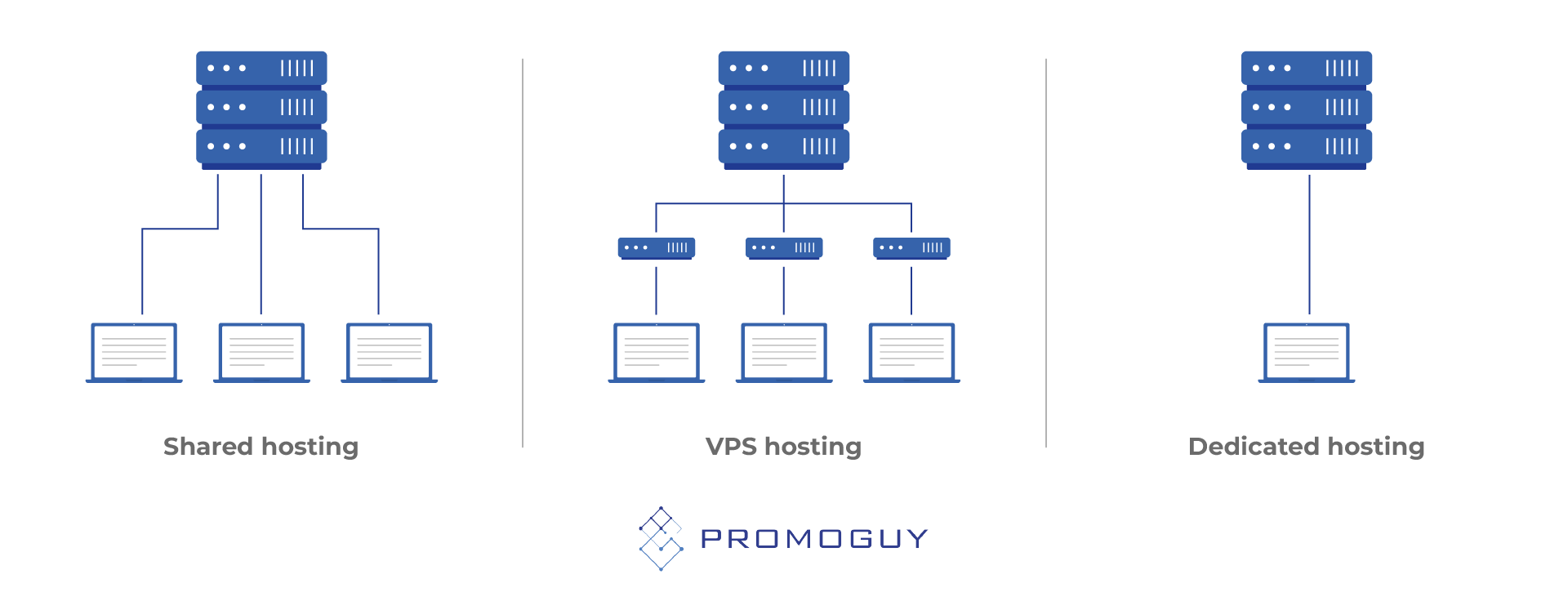
Cloud hosting comes in multiple forms as well, including:
- Public cloud: Smaller to mid-sized businesses can save costs by choosing public systems, as it is a simpler, more cost-effective solution to hosting data
- Private cloud: Generally, a larger company that can manage higher budgets can opt for a private or hybrid cloud solution. This enables better protection of private information for them and direct management of servers
- Hybrid cloud: The use of a cloud server and a physical server together. This is best for companies that have a sensitive operation structure that requires data high-level data security
- Multi-cloud: This is a form of cloud computing which operates with a combination of clouds (can be two or more public clouds, two or more private clouds, or a combination of public, private and edge clouds) to distribute applications and services
Cloud Hosting Service Benefits & Use Cases

Cloud Hosting vs Traditional Hosting & Web Platforms
There are quite a few ways cloud services surpass physical web hosting. Since website performance depends on servers, websites with a lot of traffic can require much stronger servers. Cloud web hosting offers more flexibility in terms of resource allocation, especially for high-traffic sites. As we’ve covered previously, page speeds can be a crucial part of search engine optimization.
Traditional hosting can also be less safe and secure. In the event of hardware failures or cyber-attacks, there is a higher risk of downtime and data loss. If it is a dedicated server, you have to handle the server security workloads. Cloud hosting allows for better protection due to its existence on multiple servers.
Since data is stored digitally on multiple servers in remote locations, there are more backups. Hosting providers also maintain copies of the data for faster recovery. Cloud hosting is also more scalable since many companies offer autoscaling as part of their service plans.
Similarly, managed cloud hosting is a subcategory worth mentioning for its benefits. A managed vs unmanaged cloud differs because. Managed cloud services allow companies to purchase servers in slices or as virtual servers. This further allows companies to run high-power applications at lower costs but with better security and consistency by using a hybrid of physical and digital storage.
Microsoft Cloud Background Check
Many companies use cloud hosting systems to great effect. These allow companies to not just enhance their websites and application quality, but also their security systems. Microsoft’s Cloud Background check is a perfect example of secure cloud hosting.
As part of its hiring process, Microsoft conducts a background check for the employees that manage their cloud network technologies. The access permission is logged into multiple digital servers and is easily revocable upon the employee’s exit. The cloud manages employees’ data and helps manage data across multiple outside organizations for purposes like citizenship status and criminal behaviour reporting related to their work.
Cloud Native Resource Management
Cloud-native computing allows for containers, single-purpose serverless functions, and microservices for resilient and highly flexible apps. Native cloud servers can also allow for new forms of service management and Identity Access Management, much like the Microsoft case.
Similarly, such a system allows for a number of benefits that many companies are using to their advantage:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS allows smaller companies to avoid hardware costs, the cost of the space, the electricity to power it, and the overhead to build and maintain it, instead utilizing a cloud service
- Testing & Development: Companies can build digital platforms, make changes, and tear things down easily. Gaming companies do this all the time with their resource clouds and online marketplaces that many other companies interact with as the server owners make constant updates
- Desktop as a Service (DaaS): Virtual desktops and DaaS are a handy method to standardize security and content access across devices, especially for IT teams. This can help curb some of the broader effects of a disaster such as a hack or power outage on the servers
Cloud Digital Asset Management
Cloud web hosting systems allowed for both SaaS digital asset management (DAM) and hybrid DAM. Traditionally, DAM solutions have to be on-site, which requires more infrastructural investment. Cloud and hybrid DAMs can also allow for quicker and more scalable operations on this front.
Cloud-based SaaS and DAM software are great for companies that:
- Don’t want to put heavy investment in infrastructure
- Need the option for scalability
- Have smaller teams with little IT manpower
- Aren’t ready for a heavy commitment or are just starting out
Hybrid systems also have their advantages, as they keep sensitive data on-site while allowing for SaaS digital management. The downside is that companies opting for this model will have to pay extra to maintain the physical and cloud systems simultaneously. These are best for companies that:
- Are looking for a simpler deployment
- Have sensitive data of their own or deal with very sensitive client data
- Can afford the dual-system


