The Dutch Ministry of Justice and Security through the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) recently released its Cyber Security Assessment for 2019. The document details how the Dutch government is looking to mitigate threats to cyber security, ensuring the resilience of Internet protections and ensuring the average citizen’s data is safe. Here are the key takeaways from the document:
Cyber Attacks & Crime Concerns
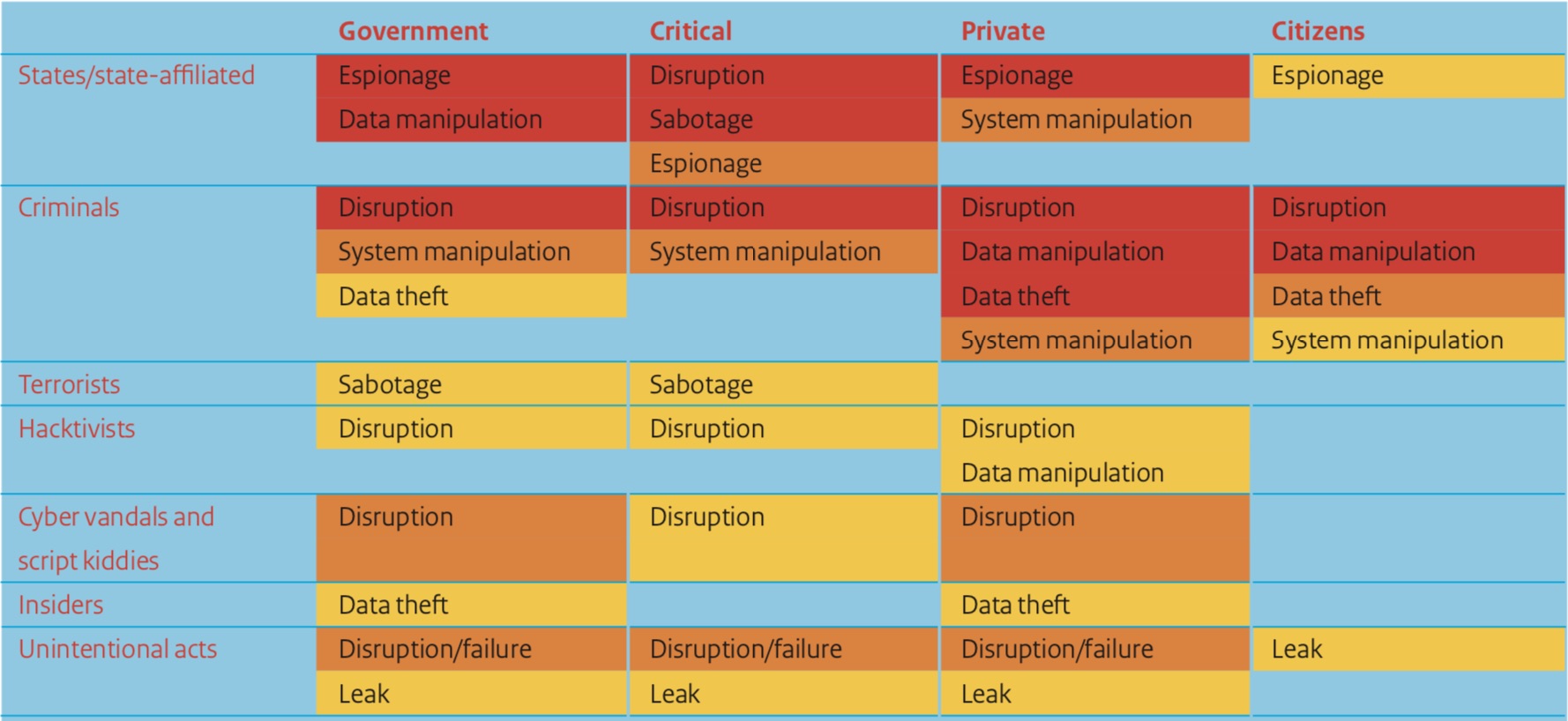
A large part of the assessment goes into great length about the risks to cyber security that result largely from nation-state actors. The main threats as outlined by the assessment come from Russia, Iran, and China. Cyber espionage, as the report outlines, is often carried out against the Dutch government and can be a means of economic growth and geopolitical influence. This is often done through malware that affects critical infrastructure, as has happened to Polish energy and transport firms in the past year. Such instability is a cause for concern, according to the Dutch Cyber Security Assessment analysts.
While the international threat has risen, there is a marked decrease in influence in terms of lone actors and cyber terrorists. On the bright side, the report seems to confirm the dwindling influence of attacks from singular individuals. Terror groups are also far less reliant on the Internet as a means of furthering their goals, at least when compared to earlier periods. Although, the increased number of diverse hacking methods has now made it difficult to identify organisations, nations or individual actors. As with most things on the Internet, sourcing and discovering the origins of malware or viruses is still an obstacle.
Another prevalent fear due to the changing technological landscape is that of shifting targets due to new technologies. This means that the increasing usage of advents like IoT (Internet of Things), cloud applications, and more digitisation of items that wouldn’t otherwise have a digital connection has led to concerns about more things being hackable. This digitisation makes these particular data carriers prominent targets for information theft and exploitation.
Digital Interconnectivity Higher Than Ever Before

While interconnectivity has brought in some negatives like the ones mentioned above, the report also stresses some even-handed positives. That is why various initiatives are being tested and funded to further increase and harness the power of such connectivity. €165 million has been set aside to make communication between citizens, entrepreneurs and the government smarter, more accessible and more personal. The government has also earmarked €60 million for digital care to promote the use of e-health and further boost information exchange. These are prominent factors contributing to economic growth across the globe. However, the distribution of profits is still going to tech monopolies.
The Dutch Cyber Security Assessment also stresses that, while the level of interconnectivity between services has increased, Social media platforms and other such net applications are increasingly dominated by big tech monopolies. As a result, even though there is a whole range of varying apps, cloud platforms, and websites, a lot of them are dominated by the same big names like Google and Facebook, who each own many different subsidiaries. This imbalance is pretty remarkable as it has resulted in Facebook (including WhatsApp and Instagram), Amazon, Apple, Google and Microsoft holding a combined market share of 95%.
An increasing number of digital services, such as online bookkeeping and authentication services, are based on an underlying cloud platform belonging to one of the major players (e.g. Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud). This further increases dependence on these suppliers and leads to some complications for businesses, as switching from one cloud platform to another can be expensive.
Government Solutions Being Implemented

Various governments have been very vocal, according to the report. The US government has been vigilant against Russian and Chinese cyber attacks and has allegedly authorised activities aimed at compromising Russian networks in order to prevent possible cyber attacks on the US as a response to potential election hacking. These measures have put some strain on various communications between Russian and American firms, even implicating known international hacker groups.
Similarly, in December 2018, the Czech National Cyber and Information Security Agency (NCISA) issued a warning against hardware and software produced by the Chinese companies Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd and ZTE Corporation. According to the NCISA, the use of hardware and software supplied by these companies constituted a threat to national security. Businesses designated as critical national infrastructure, important information systems and essential providers are obliged to take note of this warning and to implement adequate countermeasures.
These are major changes in the landscape of cyber-security and international relations. Companies are affected by such changes because they may not be able to simply do business unrestricted with such regions in the future, owing to stricter cyber-security laws. As the Internet opens up communication lines, it is also producing tons of headaches for security professionals, businesses, and regular users. Measures to curb such damages will naturally result in some growing pains till properly adjusted.
Related Article: Social Media Predictions to Keep in Mind For 2020



One Reply to “Dutch Cyber Security Assessment 2019 Key Takeaways”
What is Defi: Decentralised Finance & Blockchain Explained - Promoguy
February 23, 2021
[…] when it comes to industries and data security, a body of data implies that lack of data transparency and over-reliance on centralised databases is a major issue. Modern digital ledgers can help solve such problems and balance transparency […]
Comments are closed.