Properly cultivating one’s online presence is practically impossible these days without a decent understanding of Google Analytics. The service, if used correctly, can act as the primary hub for analysing your digital footprint, web traffic rates, and keeping track of your advertising ROI. All the free tools it provides are a powerful asset and we’re here to walk you through the basics.
Google Analytics 101
Getting started with Google Analytics is as easy as setting up an account on the website and adding a tracking code. Users can do this with any Google account but considering the pertinent nature of the information, it’s best to create a new, secure email address (or multiple ones). Thankfully, the service accommodates a broad range of options for managing your business and personal websites.
Users can run a fairly large number of websites under one account, managing them through one email address. This can be handy if you need to operate a brand name that has a lot of varying operations and especially if it has multiple distinct storefronts. Managing these websites through one separate account can also be useful for precisely comparing data analytics per branch and measuring the levels of success against each other.
You can put up to 50 websites under one business account, so it’s best to make use of the feature when necessary. These accounts can be added in the admin menu, the basics are set up. Conversely, you could set up different accounts for all your businesses if that seems more manageable since the Analytics service is entirely free. It’s best to organise your data in the way that best suits your work style.
Installation Methods
The type of installation that is most suitable for you will vary on the type of website you’re planning on running. After receiving a tracking ID, you will also get a Google Analytics code. You need to insert this code into every page that you wish to keep track of, however, the installation types may vary.
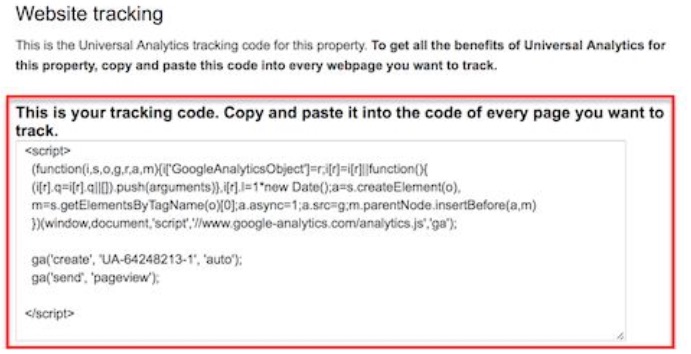
CMS programs like WordPress (particularly the Genesis framework) have a header and footer script where such a code can be placed. Another easy method of installing Analytics on your chosen CMS is the Yoast plugin, which should easily apply to the software despite the framework and themes. Websites like Tumblr have an edit theme button where you can find a place to put in the code. For commerce stores like Shopify, you simply have to paste the code where it specifies.
Websites running on HTML files have a slightly different protocol. You can add the tracking codes before the </head> tag on each of the pages you want to track. One convenient way of doing this is by using a text editor program such as TextEdit or Notepad. You can then upload the file to whatever web host you have using an FTP program.
While they may vary, most methods of inserting the tracking code are quite easy. For other types of websites, there is an abundance of information available online and most of them will guide you through it.
The next step is to set up your goals so that analytics can keep track of conversions to certain pages. Goals can vary from purchases to email list sign-ups to form completion. For example, very often, designers will set up a thank you page for purchases or visits, which can be set as the destination that is being tracked. Keeping track of this helps your website traffic stats and, in the case of purchases, revenue. You can further simplify this by adding a monetary value to the page visits or certain interactions (if applicable).
Viewing Your Data
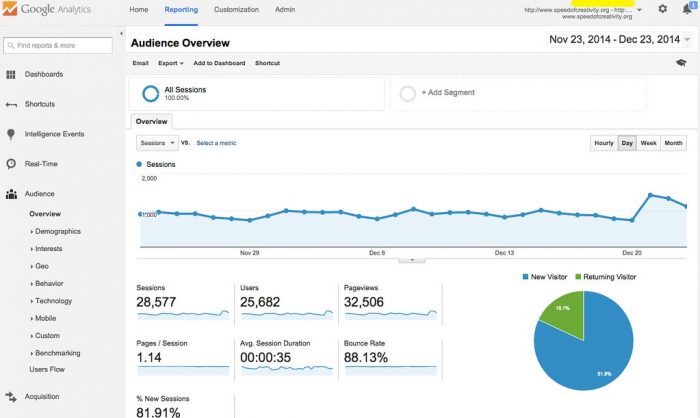
When you log in to Google Analytics, the primary page will be your Audience Overview report, unless you have multiple pages to choose from (in which case you’ll have to pick a specific site first). This page is one of over 50 different reports Google Analytics offers. Different reports are accessible through the Reporting link at the top.
Here, you can click on date ranges, the number of sessions over time or other variables to get more specific data or compare periods with each other. Aside from these metrics, you can also view the top ten languages, countries, cities, browsers, operating systems, services providers, and screen resolutions your visitors are using.
Each of these reports has more comprehensive breakdowns within it, which you can access by clicking on the data. More precise breakdowns can even inform you of what specific province or state visitors are from within a country. These metrics help improve your ability to cater to customers. find new ones and keep track of your conversions.
Types of reports include:
- Audience reports: Viewer data like Demographics (age, gender), general interests, location, preferred language, behaviour characteristics like how often they visit your site, and what technologies they use to access it.
- Acquisition reports: This is where you can see what drove visitors to your website. You can view how traffic from social networks draws you in. It also allows users to connect Google Analytics to AdWords and to Google Webmaster Tools / Search Console to learn more about search traffic.
- Behaviour reports: Here you can check what your top sites/pages are in terms of both entry and exit. You can also view the loading speeds and what terms users searched for to arrive at your web pages.
There’s a whole lot more to this complex and efficient analytics tool but this guide should give you everything you need to start off.
Related article: Why do I need Online Marketing?



One Reply to “Google Analytics: A Beginner’s Guide to Setting Up”
GA4: What is Google Analytics 4 & How to Use it - Promoguy
July 6, 2021
[…] We’ve already published a Google analytics starter guide before, so this article isn’t that. If you’re looking for a guide on the basics of how […]
Comments are closed.